class a foam acts as a surfactant which means that it
A product that relies primarily on the water it contains for firefighting. This gives the solutionwater the ability to spread and penetrate into Class A materials.

Stability Of Foam An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
1 Type of foam concentrate used.

. Firefighting foam is a foam used for fire suppressionIts role is to cool the fire and to coat the fuel preventing its contact with oxygen resulting in suppression of the combustionFire-fighting foam was invented by the Russian engineer and chemist Aleksandr Loran in 1902. An example would be like cooling a glass of water with a single ice cube. Class A foams may be used as a firefighting agent or as a fire barrier.
Class A foams are blend of surfactants that enable strong wetting and foaming properties. The first reason surfactants help create foams is that the surface becomes elastic. Anionic surfactants create a lot of foam when mixed.
These products contain foaming agents which create air bubbles when aerated and wetting agents which allow the fluid that drains from foam bubbles to be easily absorbed by fuel soil and other materials that it come into contact with. Class A foam surfactants stabilize liquid films foam bubbles in three ways. A foam concentrate containing fluorochemical surfactants that control the physical properties of water enabling it to float and spread across the surface of the hydrocarbon liquid.
AFFF Aqueous Film Forming Foam. The rate of application for class B foam depends on what five factors. These proportioning rates make the use of Class A foam a cost effective means of combating fires because relatively small amounts of foam concentrate can be used to make effective foam.
Hi Jim917 My department is paying 1750 per gallon or 8750 per 5 gallon pail. The surfactants used must produce foam in concentration of less than 1. Class A foam is deployed through a variety of portable and fixed appliance.
Surfactants may act as detergents wetting agents emulsifiers foaming agents or dispersants. It also gives water a foaming ability which allows water to remain and cling to vertical and horizontal surfaces without run. As foam generation and also foam stability is a dynamic for process for generating and reducing surface area in a surfactantwater system the diffusion of the surfactant to the surface and the change in surface coverage at least locally during bubble generation and drainage of the film is a more useful way of explaining foam properties.
Class A foam will increase wetting effectiveness which allows for greater penetration into Class A fuels. 2 Whether the fuel is on fire. The word surfactant is a blend of surface-active agent coined c.
Class A foam is for use against Class A fires such as paper rubber textiles and wood. We are injecting at a rate of 3 of class A foam per 100 gallon of water. The surfactants in the foam solution increase the wetting effectiveness of the water draining from the foam blanket.
Other components of fire-retardant. So a surfactant which reaches the lowest surface tension for the least amount of surfactant is in general going to give an easier longer-lasting foam. Qualified to USDA Forest Service 5011-307a and UL approved for use as a wetting agent for Class AB applications.
5 foam application via fisxed system or portable equipment. Environmentally responsible KnockDown a Class A foam concentrate is a unique formulation providing unmatched firefighting performance and flexibility. It is proportioned by a FoamPro 2002 proportioner.
With the CAFS application we are extinguishing an average room and contents with about a 12. The energy need to increase the surface area A is γδAδt so a low γ means more foam for less energy. ADVANTAGES OF CLASS A FOAM Wetting Characteristics.
Aqueous film forming foam AFFF means a fluorinated surfactant with a foam stabilizer which is diluted with water to act as a temporary barrier to exclude air from mixing with the fuel vapor by developing an aqueous film on the fuel surface of some hydrocarbons which is capable of suppressing the generation of fuel vapors. Surfactants are compounds that lower the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids between a gas and a liquid or between a liquid and a solid. In addition the portion of the foam concentrate molecule that repels other water in order.
We use the Class A foam with CAFS system. Water Foam Class A concentrate is simply a surfactant similar to dishwashing soap that reduces surface tension. Class A foam is biodegradable and non-toxic so it is environmentally sustainable.
3 type of feul hydrocarbonpolar solvent 4 whether fuel is spilled or contained in tank. A pure water surface has no such elasticity and the bubbles break quickly. Class A foams are often intended for use at very low concentration of 01 to 1 and are formulated using environmentally favourable raw materials.
The pressure inside a foam of radius R that contributes to its self-destruction is 2γR. Anionic surfactants have a negative charge on their hydrophilic end. Class A Foams National Foams Class A Foams are also wetting agents.
When used as a wetting agent the concentrate lowers the surface tension of the water allowing better penetration into deep seated fires. When added to water the resulting foam solution consists of many smaller droplets with much more surface area allowing faster heat absorption. Because they are able to attack a broad range of soils anionic surfactants are used frequently in soaps and detergents.
Class A foam is primarily a surfactant which is to say that it breaks down the surface tension of water. As a fire barrier Class A foams increase moisture con-tent in Class A combustibles preventing the ignition of these type fuels. Give the bubble film a viscosity that minimizes drainage.
The negative charge helps the surfactant molecules lift and suspend soils in micelles. What is a Class A Foam. This means that the bubbles can withstand being bumped squeezed and deformed.
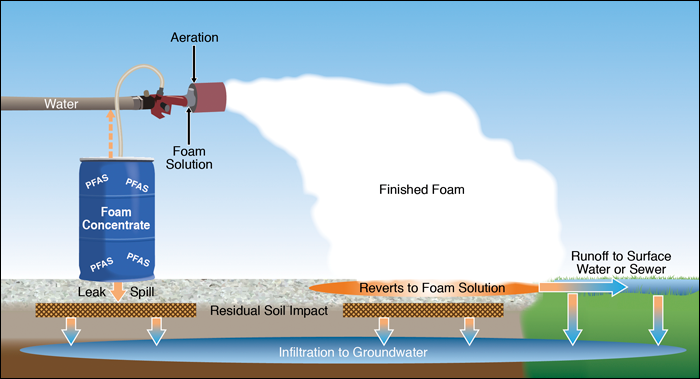
3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances

Pemadam Api Wikipedia Bahasa Indonesia Ensiklopedia Bebas

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex

Surface Active Agents Surfactants Types And Applications
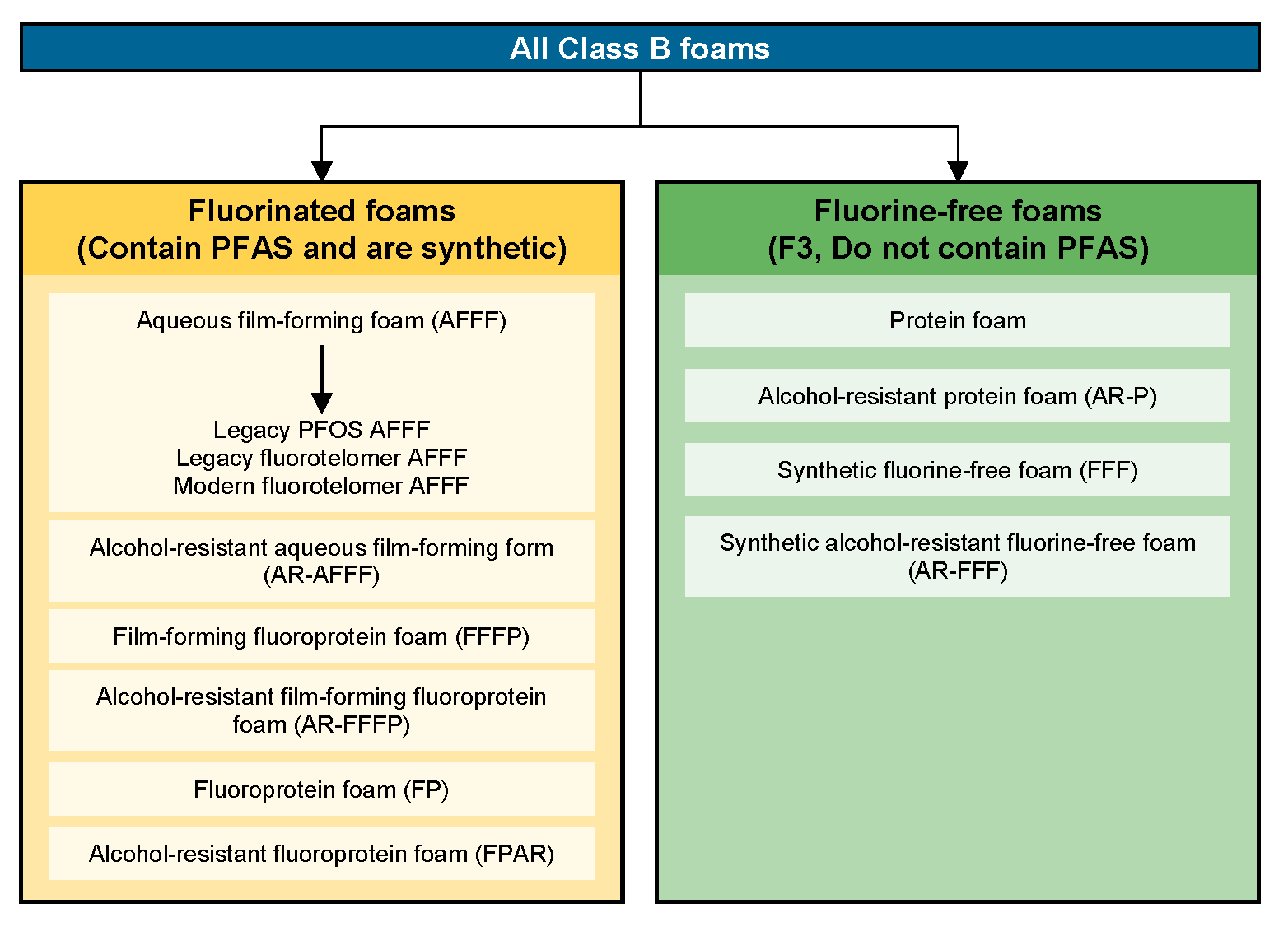
3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances

Types Of Firefighting Foam Vanguard Fire And Security

Despite Advantages Of Using Class A Foam To Battle Wildfires Use Is Down That Needs To Change International Fire Fighter
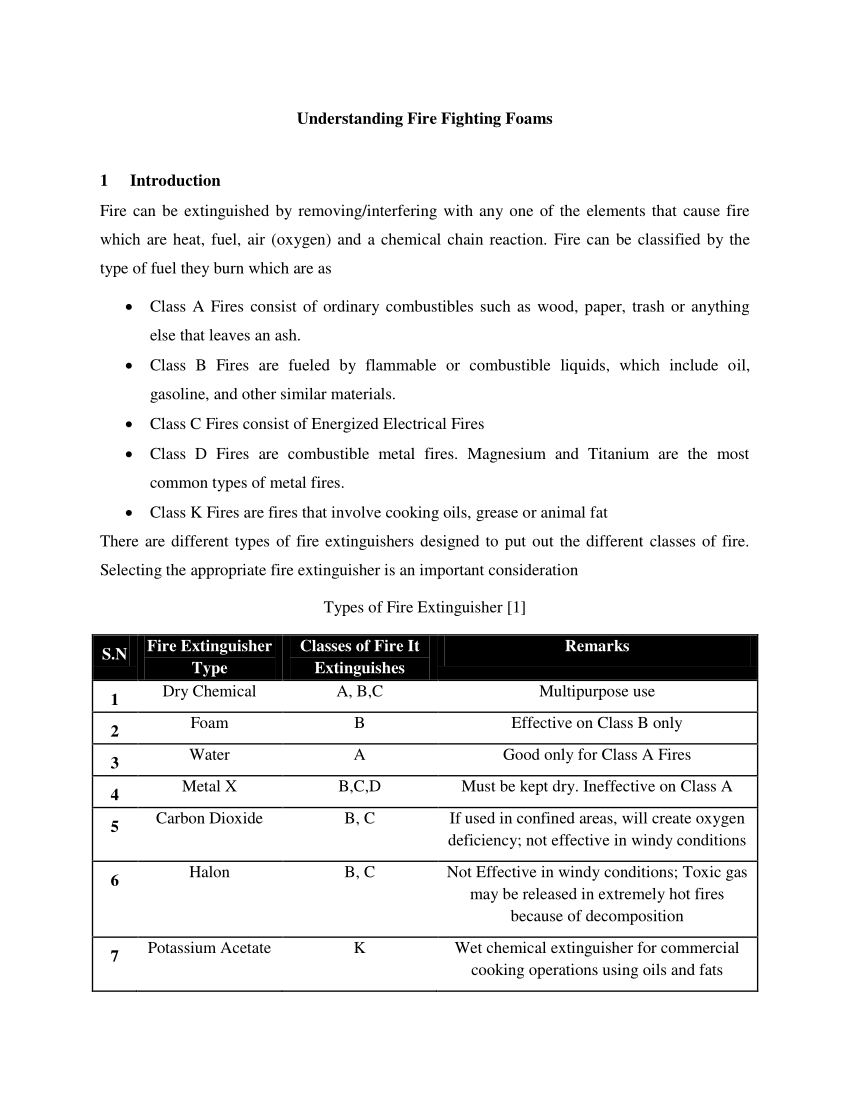
Pdf Understanding Firefighting Foams

5 Natural Surfactants For Use In Organic Cosmetics Formula Botanica
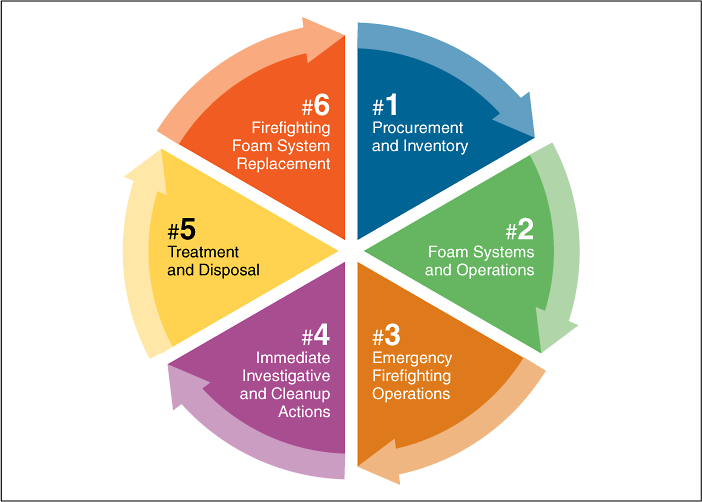
3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances

Surface Active Agents Surfactants Types And Applications

What Are Surfactants Surfactants Meaning Types Of Surfactants Surfactant Examples Anionic Surfactants
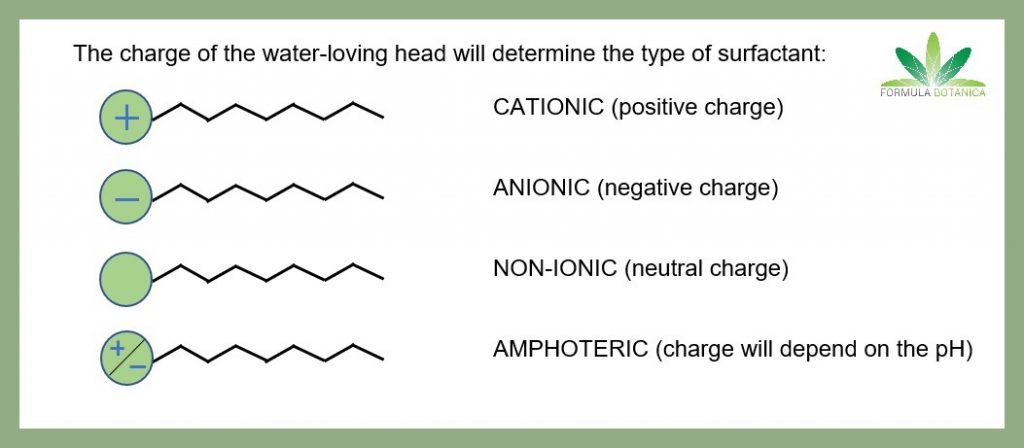
5 Natural Surfactants For Use In Organic Cosmetics Formula Botanica

Surface Active Agents Surfactants Types And Applications

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex

